- 11/02/2026
- MyFinanceGyan
- 21 Views
- 1 Likes
- GST
GST on Residential Property Rent – Who Is Liable to Pay Tax?
The applicability of GST on residential property rent has been a subject of confusion, especially after key amendments under the GST regime. Landlords, tenants, and businesses often struggle to determine whether GST is applicable, who is liable to pay it, and when exemptions apply.
This article explains GST on residential property rent with a focus on taxability, liability, exemptions, reverse charge mechanism (RCM), and compliance requirements.
Renting of Property Under GST Law:
Under the GST framework, renting of immovable property is treated as a supply of service. However, not every renting transaction attracts GST. Taxability depends on several factors, including:
- Nature of the property
- Purpose for which the property is used
- GST registration status of the landlord and tenant
Residential property rent enjoys specific exemptions, but these are subject to strict conditions.
Is GST Applicable on Residential Property Rent?
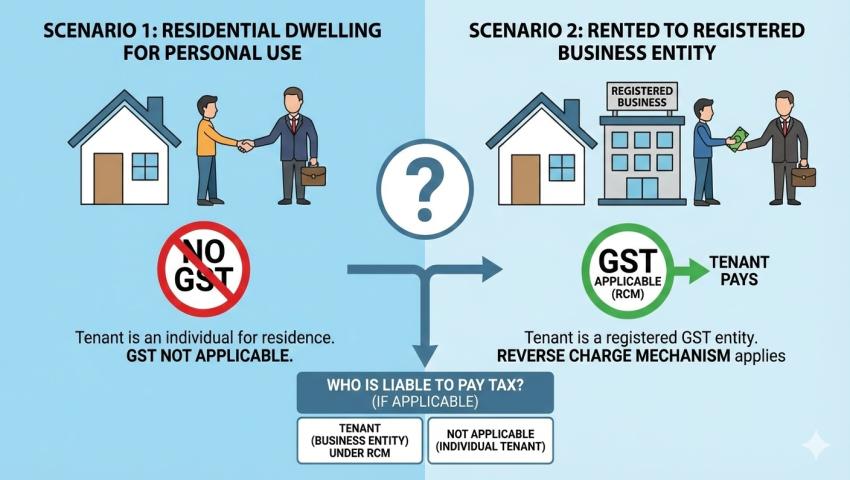
As a general rule, GST is not applicable on rent of residential property when it is used for residential purposes.
GST law specifically exempts the renting of a residential dwelling for use as a residence. This exemption applies irrespective of whether the landlord is registered under GST or not, provided the property is used purely for residential living.
When Is Residential Rent Exempt from GST?
GST exemption applies when all the following conditions are satisfied:
- The property qualifies as a residential dwelling
- The property is rented for residential use
- It is actually used as a place of residence
Common Exempt Scenarios:
- Renting a flat or house for personal living
- Leasing a residential property to an individual for residential use
In such cases, no GST is payable by either the landlord or the tenant.
When Does GST Apply on Residential Property Rent?
GST becomes applicable in certain specific situations where the exemption conditions are not met
1. Residential Property Used for Commercial or Business Purpose:
If a residential property is rented out for commercial or business use, the GST exemption does not apply.
Examples:
- Residential flat used as an office
- Guest house or service apartment
- Paying guest (PG) accommodation operated as a business
In such cases, GST is chargeable on the rental income.
2. Renting to a GST-Registered Person – Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM):
A significant change under GST is the introduction of Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) for certain residential rental transactions.
GST under RCM applies when:
- A residential property is rented to a GST-registered person, and
- The property is used for business or commercial purposes
Implications:
- GST is payable under RCM
- Tenant (registered person) is liable to pay GST
- Landlord does not charge GST in the rent invoice
Applies even if the landlord is unregistered
Who Pays GST on Residential Property Rent?
The liability to pay GST varies based on usage and registration status.
Understanding this distinction is essential for proper compliance.
GST Rate on Residential Property Rent:
Where GST is applicable, the rate is:
- 18% (9% CGST + 9% SGST) for intra-state transactions
- 18% IGST for inter-state transactions
The rate applies to the rent amount specified in the agreement.
Input Tax Credit (ITC) on Residential Rent:
The availability of input tax credit depends on the purpose of use.
ITC Allowed:
- When the property is used for business purposes
- When GST is paid under RCM by a registered tenant
ITC Not Allowed:
- When the property is used for personal residence
- When the rental income is exempt from GST
Proper tax invoices and payment records are necessary to claim ITC.
GST Registration Requirement for Landlords:
A landlord is required to obtain GST registration if:
- GST is payable under forward charge, and
- Aggregate turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold limit
However, registration is not required solely for exempt residential rent or where GST is payable by the tenant under RCM.
Common Misconceptions About GST on Residential Rent:
Some frequently held but incorrect beliefs include:
- GST applies to all residential property rentals
- Landlords always pay GST
- GST applies even when the property is used for personal residence
- Unregistered landlords are always exempt
Such misconceptions often lead to incorrect tax treatment and compliance issues.
Practical Illustration:
Consider the following situations:
- Residential flat rented to an individual for living → No GST
- Residential flat rented to a company for office use → GST applicable
- Residential flat rented to a GST-registered firm for business use → GST payable by tenant under RCM
These examples clearly demonstrate how GST liability varies.
Compliance Tips for Landlords and Tenants:
- Clearly specify the purpose of use in the rental agreement
- Verify the GST registration status of the tenant
- Monitor applicability of RCM provisions
- Maintain proper agreements, invoices, and records
Proper documentation helps avoid disputes, interest, and penalties.
Conclusion:
GST on residential property rent depends primarily on how the property is used and who the tenant is. While rent for personal residential use is fully exempt, GST becomes applicable when the property is used for commercial purposes or rented to a GST-registered person under the reverse charge mechanism.
Understanding who pays GST on residential rent ensures correct compliance for both landlords and tenants, helping avoid unnecessary tax exposure and litigation.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, tax, or professional advice; readers are advised to consult a qualified tax professional for guidance specific to their situation.