- 28/10/2025
- MyFinanceGyan
- 447 Views
- 1 Likes
- Share Market
How to Use RSI and Moving Averages Together for Better Entry Signals: A Complete Guide
In the fast-paced world of stock and forex trading, knowing when to enter a trade can make all the difference. Two of the most powerful and time-tested indicators — the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Averages (MA) — can be combined to create highly accurate entry signals.
When used together, these tools offer a perfect balance between momentum detection and trend confirmation, helping traders reduce false signals and improve their win rate.
This comprehensive guide explains how to effectively use RSI and moving averages together, covering their basics, combination strategies, risk management techniques, and practical tips for consistent trading success.
Understanding RSI and Moving Averages
What is RSI (Relative Strength Index)?
The RSI, developed by J. Welles Wilder, is a momentum oscillator that measures the strength and speed of price movements on a scale of 0 to 100.
- Above 70: The asset is considered overbought, signaling a possible pullback or reversal.
- Below 30: The asset is considered oversold, suggesting a potential upward bounce.
- Divergences: When price and RSI move in opposite directions, it often indicates weakening momentum and possible trend reversal.
What are Moving Averages (MA)?
Moving averages smooth out price data over a period of time to identify overall trends.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Averages price over a fixed number of periods.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices for quicker responsiveness.
Common choices include 20-day, 50-day, and 200-day MAs, depending on the trading timeframe.
Moving averages help traders:
- Identify trend direction (price above MA = uptrend; below = downtrend).
- Spot trend reversals using crossovers between short and long MAs.
- Determine dynamic support and resistance zones.
Why Combine RSI and Moving Averages?
Using RSI or moving averages in isolation can sometimes lead to false entries. Combining them, however, filters noise and provides higher-probability setups.
Here’s why this combo works:
- RSI = Momentum gauge: Tells you if buyers or sellers are in control.
- MA = Trend filter: Confirms the dominant direction of the market.
- Together = Strong signal confirmation: Trade only when momentum and trend align.
This synergy ensures that you enter trades with the prevailing trend rather than against it.
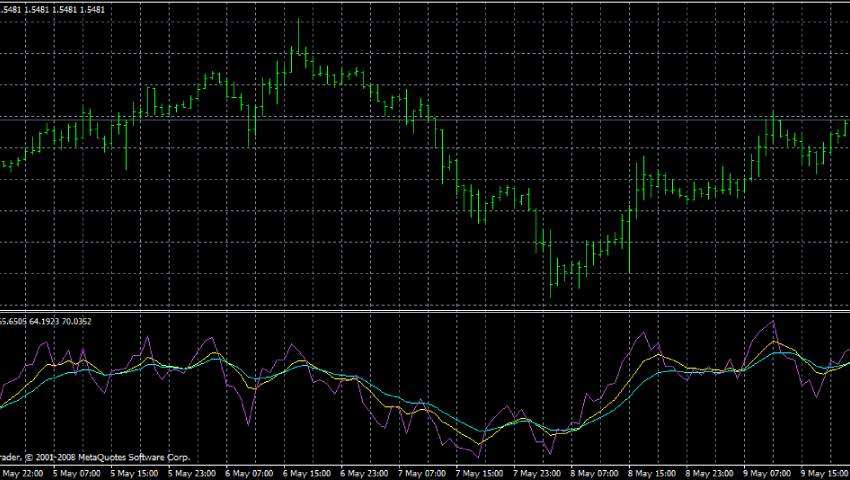
How to Use RSI and Moving Averages for Entry Signals?
Step 1: Identify the Trend Using Moving Averages
Start with the bigger picture — determine whether the market is trending up or down.
- Go long (buy) only when the price is above a major moving average (like 50-day or 200-day).
- Go short (sell) when the price is below it.
- You can also look for moving average crossovers (e.g., 10 EMA crossing above 20 EMA) to catch emerging trends early.
This step ensures you avoid countertrend trades — a common mistake among new traders.
Step 2: Time Your Entry with RSI
Once the trend is confirmed, use RSI to pinpoint the best entry moment.
- In an uptrend: Wait for RSI to pull back to the 30–40 range (temporary weakness) and then cross back above it — indicating momentum recovery.
- In a downtrend: Watch for RSI to rise to 60–70 and then cross back below — showing momentum is turning bearish again.
Combining RSI levels with moving average confirmation gives you a precise, rule-based entry point.
Step 3: Confirm and Execute
For long entries:
- The short-term MA crosses above the long-term MA (bullish crossover).
- RSI crosses above 50 or rebounds from oversold territory.
- Look for a bullish candlestick pattern (like engulfing or hammer) for added confirmation.
For short entries:
- The short-term MA crosses below the long-term MA (bearish crossover).
- RSI dips below 50 or falls from overbought levels.
- Confirm with a bearish candle near the crossover.
This three-step confirmation — trend + momentum + price action — helps filter out false breakouts.
Example Strategy: The 10/20 EMA with RSI Setup
This simple and widely used strategy is great for both swing and intraday traders.
Indicators:
- 10-period EMA
- 20-period EMA
- 14-period RSI
Buy Setup:
- 10 EMA crosses above the 20 EMA (trend turning bullish).
- RSI crosses above 50 or rises from below 40.
- Enter on the candle close confirming both signals.
- Place stop loss below recent swing low or 20 EMA.
- Set profit target near previous resistance or use a trailing stop behind EMAs.
Sell Setup:
- 10 EMA crosses below the 20 EMA (trend turning bearish).
- RSI crosses below 50 or drops from above 70.
- Enter on candle close confirming both conditions.
- Stop loss above recent swing high or 20 EMA.
- Target previous support or use a trailing stop.
Advanced Tips for Combining RSI and Moving Averages:
- Use Multiple Timeframes: Confirm the trend on a higher timeframe (like daily) using moving averages, and fine-tune entries on a lower timeframe (like 1-hour) with RSI signals.
- Watch for RSI Divergences: If price makes higher highs but RSI doesn’t, momentum is weakening — a potential reversal sign. Combined with a moving average crossover, this can be powerful.
- Look for Confluence: Align RSI signals with moving averages, support/resistance zones, or Fibonacci levels for stronger setups.
Risk Management and Trade Discipline:
Even perfect signals can fail — so protect your capital first.
- Always use stop-loss orders below/above key technical levels.
- Risk only 1–2% of your capital per trade.
- Define take-profit levels or use trailing stops.
- Avoid trading without both trend and momentum alignment.
Disciplined risk management ensures survival through inevitable drawdowns.
Conclusion:
Combining RSI and moving averages gives traders a balanced and systematic approach to identifying high-probability trade entries.
- Moving averages confirm the trend.
- RSI fine-tunes entry timing.
This dual approach reduces emotional decision-making and increases consistency — whether you trade stocks, forex, or crypto.
By applying these tools together with sound risk management, traders can navigate any market environment with confidence and precision.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are for educational purposes only. They reflect the author’s personal opinions and are not intended as investment advice or product recommendations.



