- 20/02/2026
- MyFinanceGyan
- 14 Views
- 0 Likes
- Company Law
Appointment of Additional Director: Process, Legal Provisions, and Practical Guide
As businesses grow and evolve, the need for additional expertise, strategic guidance, or compliance-driven board strength often arises. One of the most efficient ways to meet this requirement is through the appointment of an additional director. This mechanism allows companies to induct new directors quickly without waiting for the next Annual General Meeting (AGM).
Understanding the appointment of additional director under the Companies Act, 2013 is essential for directors, promoters, compliance officers, and professionals. While the process is relatively straightforward, it must strictly comply with statutory provisions to remain valid.
This article explains the meaning, legal framework, eligibility, procedure, tenure, and key compliance aspects related to the appointment of an additional director in a company.
What Is an Additional Director?
An Additional Director is a director appointed by the Board of Directors between two Annual General Meetings. This appointment is temporary in nature and is made to address immediate business or governance needs.
Unlike regular directors, additional directors are appointed directly by the Board, provided the company’s Articles of Association (AOA) authorize such an appointment.
Legal Provisions Governing Appointment of Additional Director:
The appointment of an additional director is governed by Section 161(1) of the Companies Act, 2013.
According to this provision:
- The Board of Directors may appoint an additional director
- Such appointment must be authorized by the Articles of Association
- The additional director holds office only up to the next AGM
This provision offers flexibility while maintaining shareholder control.
When Is Appointment of an Additional Director Required?
The appointment of an additional director is commonly used in situations such as:
- Expansion of business requiring new expertise
- Induction of investor or nominee representatives
- Replacement due to sudden resignation or death of a director
- Strengthening corporate governance
- Compliance with regulatory or contractual requirements
This mechanism helps companies respond swiftly to changing business needs.
Eligibility Criteria for Appointment of Additional Director:
Before proceeding with the appointment of an additional director, the proposed individual must meet the following eligibility criteria:
- Must be an individual (not a body corporate)
- Must have a valid Director Identification Number (DIN)
- Must not be disqualified under Section 164 of the Companies Act
- Must give consent to act as a director
Failure to meet these conditions may render the appointment invalid.
Role of Articles of Association (AOA):
The Articles of Association play a crucial role in the appointment of an additional director.
- If the AOA authorizes the Board to appoint additional directors, the Board can proceed
- If the AOA does not contain such provision, it must be amended by passing a special resolution
Checking the AOA is the first and most important step in the process.
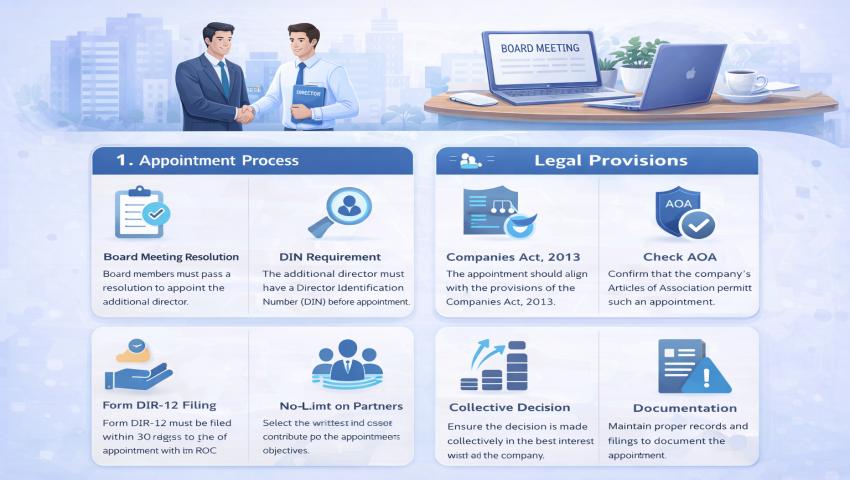
Step-by-Step Process for Appointment of Additional Director:
Step 1: Verify Authorization in AOA:- Confirm that the Articles of Association allow the Board to appoint additional directors. If not, amend the AOA before proceeding.
Step 2: Obtain Director Identification Number (DIN):- If the proposed additional director does not already have a DIN, it must be obtained by filing the appropriate form along with identity and address proofs. A director cannot be appointed without a valid DIN.
Step 3: Obtain Consent to Act as Director:- The proposed additional director must submit Form DIR-2, giving consent to act as a director of the company. This ensures voluntary acceptance of responsibilities.
Step 4: Declaration of Non-Disqualification:- The individual must also submit Form DIR-8, declaring that they are not disqualified under Section 164. This declaration protects the company from appointing an ineligible director.
Step 5: Convene Board Meeting:- A Board Meeting must be convened with proper notice to all directors.
At the meeting:
- Proposal for appointment is discussed
- Resolution for appointment of additional director is passed
- Effective date of appointment is decided
The appointment takes effect from the date of the Board resolution unless stated otherwise.
Step 6: File Form DIR-12 with ROC:- The company must file Form DIR-12 with the Registrar of Companies within 30 days of the appointment.
DIR-12 includes:
- Details of the additional director
- Date of appointment
- Consent and declarations
Timely filing is mandatory to avoid penalties.
Step 7: Update Statutory Registers:- After filing with the ROC, the company must update:
- Register of Directors
- Register of Key Managerial Personnel
These registers must be maintained at the registered office.
Tenure of an Additional Director:
One of the most important aspects of the appointment of additional director is the limited tenure.
- An additional director holds office only up to the next AGM
- If the AGM is not held, the director vacates office on the date when AGM should have been held
- To continue, the director must be regularized by shareholders
This ensures shareholder oversight and democratic governance.
Regularization of Additional Director:
To continue beyond the next AGM, the additional director must be appointed as a regular director by shareholders.
This involves:
- Including the appointment item in AGM notice
- Passing an ordinary resolution
- Filing necessary ROC forms
Without regularization, the additional director automatically vacates office.
Can an Additional Director Be Reappointed?
Yes, an individual who vacates office as an additional director can be reappointed, provided:
- They are eligible
- Shareholders approve the appointment
However, repeated short-term appointments without shareholder approval are discouraged.
Appointment of Additional Director vs Regular Director:
Basis Additional Director Regular Director:
- Appointing Authority Board of Directors Shareholders
- Tenure Up to next AGM Fixed term
- Speed of Appointment Immediate Procedural
- Shareholder Approval Later required Mandatory
- Understanding this distinction helps in choosing the right method of appointment.
Common Mistakes in Appointment of Additional Director:
- Not checking AOA authorization
- Delayed filing of DIR-12
- Appointing disqualified individuals
- Failure to regularize at AGM
- Improper documentation
Such mistakes can attract penalties and invalidate board decisions.
Importance of Compliance in Appointment of Additional Director:
Proper compliance ensures:
- Legal validity of board decisions
- Protection from regulatory action
- Transparency in corporate governance
- Confidence of investors and stakeholders
An improperly appointed director may expose the company to legal risks.
Role of Professionals in Director Appointment:
Company Secretaries, Chartered Accountants, and legal professionals play a key role by:
- Verifying eligibility
- Drafting resolutions
- Managing ROC filings
- Ensuring statutory compliance
Professional assistance minimizes compliance risks.
Conclusion:
The appointment of additional director is a practical and flexible provision under the Companies Act, 2013 that allows companies to strengthen their boards without delay. When used correctly, it helps businesses adapt to growth, attract expertise, and maintain governance standards.
However, this flexibility comes with strict compliance requirements. From checking the Articles of Association to timely ROC filings and shareholder regularization, each step must be followed carefully.
Understanding and correctly implementing the appointment of an additional director ensures legal validity, operational efficiency, and long-term corporate stability.
Please note:-
The views in the article/blog are personal and that of the author. The idea is to create awareness and for educational purpose and not intended to provide any product recommendations.



